With housing becoming so expensive today in Australia, portable housing such as composite and modular buildings are a real alternative.
Direct Portable Buildings can come up with real ‘Alternative Affordable Housing Solutions’ to suit your need in almost any situation.
It doesn’t matter if you are a homeowner, investor or a person with a block of land looking for temporary accommodation until you can afford to build your dream house. You could be just simply looking for a cheaper affordable alternative to the standard suburbia 3 or 4 bedroom, 2 bath, slab on ground brick veneer dwelling.
Composite building or construction?
Composite construction is a generic term to describe any building construction involving multiple dissimilar materials. It is the most modern and effective construction method for buildings.
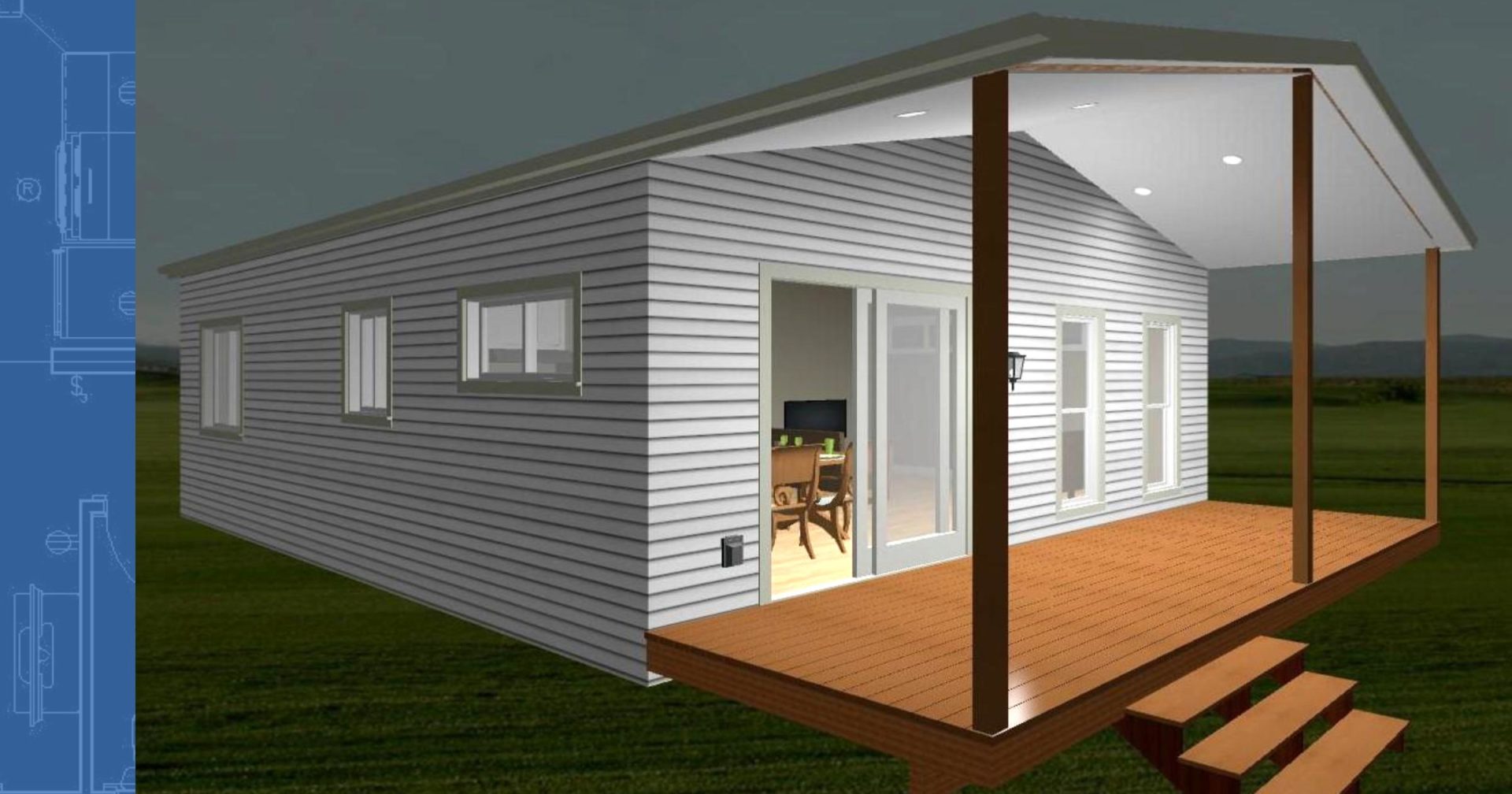
Composite buildings are delivered in two parts, and assembled at your convenient location. Floor plans can be custom designed to your specific needs.
Composite construction is often used in building construction and engineering. There are several reasons to use composite materials including increased strength, aesthetics, and environmental sustainability. It is perfectly harmonized with all international guidelines for sustainable development, supported by ongoing technological developments in steel processing, modern building materials and the countless architectural solutions provided by the steel. Over the past decades many significant buildings demonstrate the innovation and the multiple benefits offered by composite construction methods.
The main composite elements in composite buildings are:
- Steel Concrete Composite Beam
- Composite Slab
- Composite Column
We supply composite or modular buildings and modular homes consisting of repeated sections called modules.
Natural fibers
Many plastic composite building products are now produced by embedding natural fibers derived from the bast (i.e. outer stem) of certain plants—wheat-straw fiber, flax, jute, kenaf, sisal, hemp, and coconut—in a polyester or polypropylene matrix. The moderate mechanical properties of natural fibers typically prevent them from being used in high-performance applications, but their low specific weight results in relatively high specific strength and stiffness, and is generally a benefit for parts designed for bending stiffness.
Another natural fiber, wood, is used primarily in composite versions of building products such as decking, window and door profiles, decorative trim, railings, and panel products. These plastic composite building products can contain anywhere from 30 to 70 percent wood, depending on the application, with about 50 percent being typical. Regardless of the proportion, the fibers used in these plastic composites most often take the form of a particulate (e.g. wood flour), rather than the longer individual fibers commonly used with inorganic-fiber composites. Commonly used species include pine, maple, and oak.
Decking, fencing, and railings
Typically stain-resistant, waterproof, ultraviolet (UV) light-resistant, and impervious to insects, wood plastic composites can be made strong enough for applications such as load-bearing deck boards. They also tend to have good dimensional stability and a lower coefficient of expansion than solid plastics. Wood fiber, wood flour, and rice hulls are common organic fillers used in these applications.
Thanks to lower cost and easier processing, the composite building technology is becoming a practical proposition for consideration by the building industry.
Direct Portable Building’s portfolio of composite buildings are built to the highest standard and to fit all of your on-site building requirements. At Direct Portable Buildings we offer a variety of full turnkey solutions, including on-site delivery, installation, utility, interior design and decoration, services and certifications.
What is Modular building or modular construction?
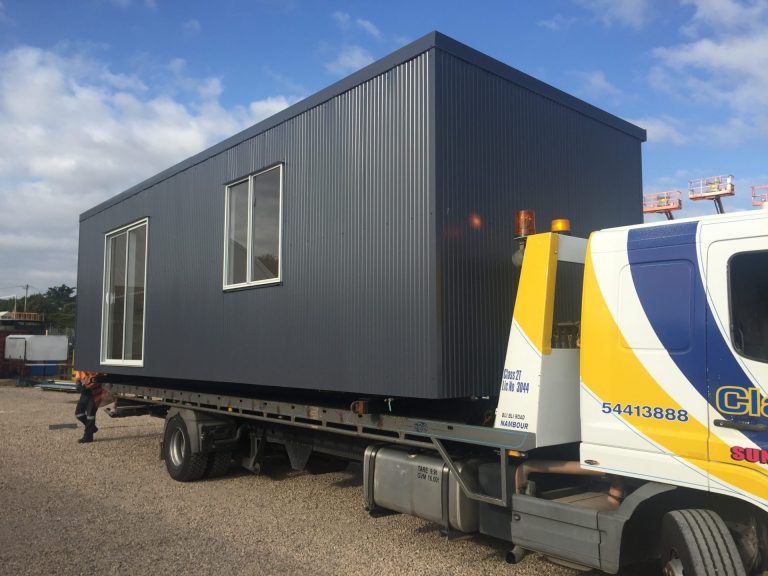
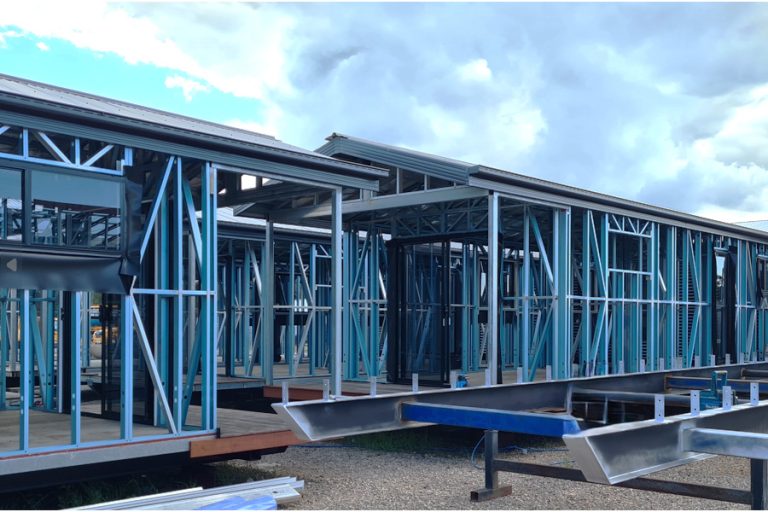
Modular construction is a process in which a building is constructed off-site, under controlled plant conditions, using the same materials and designing to the same codes and standards as conventionally built facilities – but in about half the time.
Buildings are produced in “modules” that when put together on site, reflect the identical design intent and specifications of the most sophisticated site-built facility. Construction of modular buildings occurs simultaneously with site work, allowing projects to be completed in half the time of traditional construction.
Modular buildings and modular homes are prefabricated buildings or houses that consist of repeated sections called modules. ‘Modular’ is a construction method that involves constructing sections away from the building site, then delivering them to the intended site. Installation of the prefabricated sections is completed on site. Prefabricated sections are sometimes placed using a crane. The modules can be placed side-by-side, end-to-end, or stacked, allowing a variety of configurations and styles. After placement the modules are joined together using inter-module connections, also known as inter-connections. The inter-connections tie the individual modules together to form the overall building structure.
Modular buildings are built with the same materials and to the same building codes and architectural specifications as traditional construction. Once assembled, they are virtually indistinguishable from their site-built counterparts.